Redis Cache Data Types
cache
What is Redis?
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data store known for its speed, versatility, and support for various data structures. It serves as a key-value store, message broker, and caching layer, offering high performance and scalability for a wide range of use cases in modern software development.
DataStructures supported by Redis
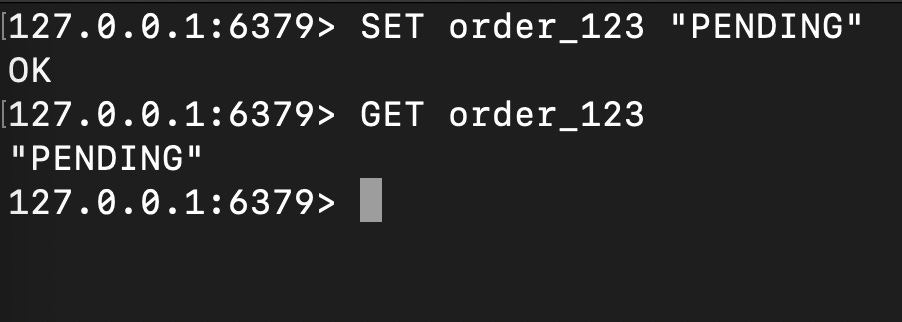
Strings
These are simple key-value pairs where both the key and value are strings. They can store text, integers, or binary data.
These can be used for values like text, hex, JSON, Binary, and other serialized objects (XML, etc.).
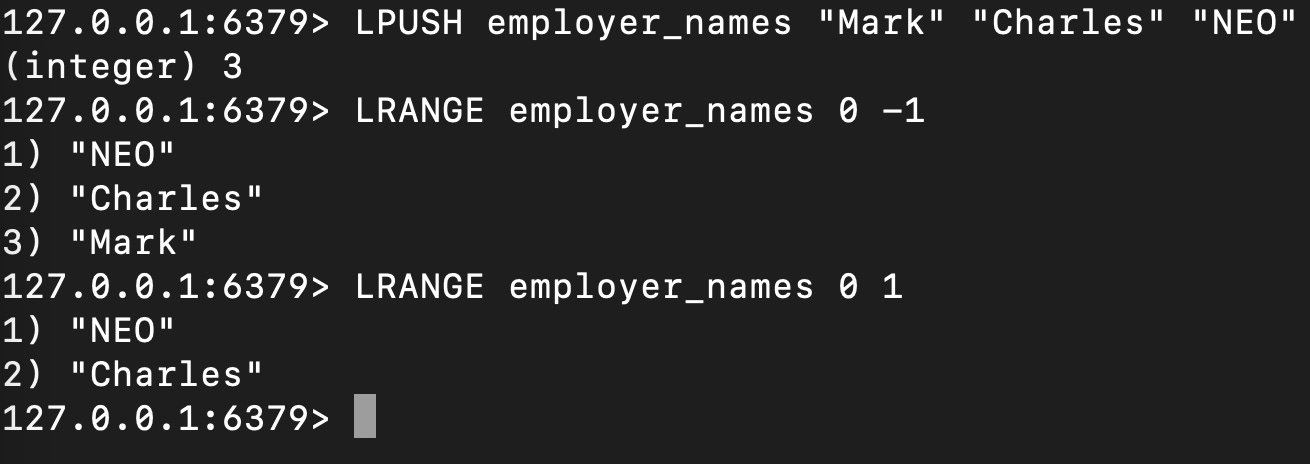
List
Lists are collections of ordered elements, where elements can be added or removed from either end of the list. Lists are implemented using linked lists.
These can be used for implementing queues, stacks, maintaining ordered sequences of data, task lists, and message queues.
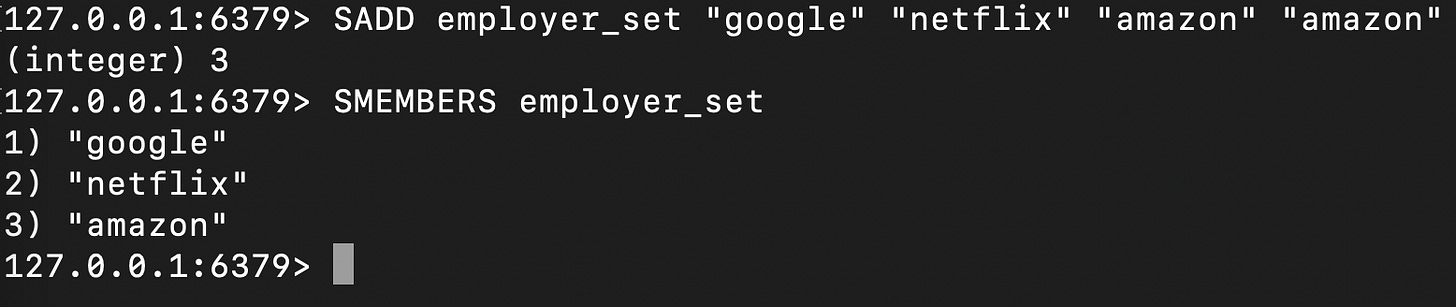
Sets
Sets are unordered collections of unique elements. They do not allow duplicate elements.
These can be used for representing relationships, performing set operations (union, intersection, difference), tracking unique elements, and implementing tag systems.
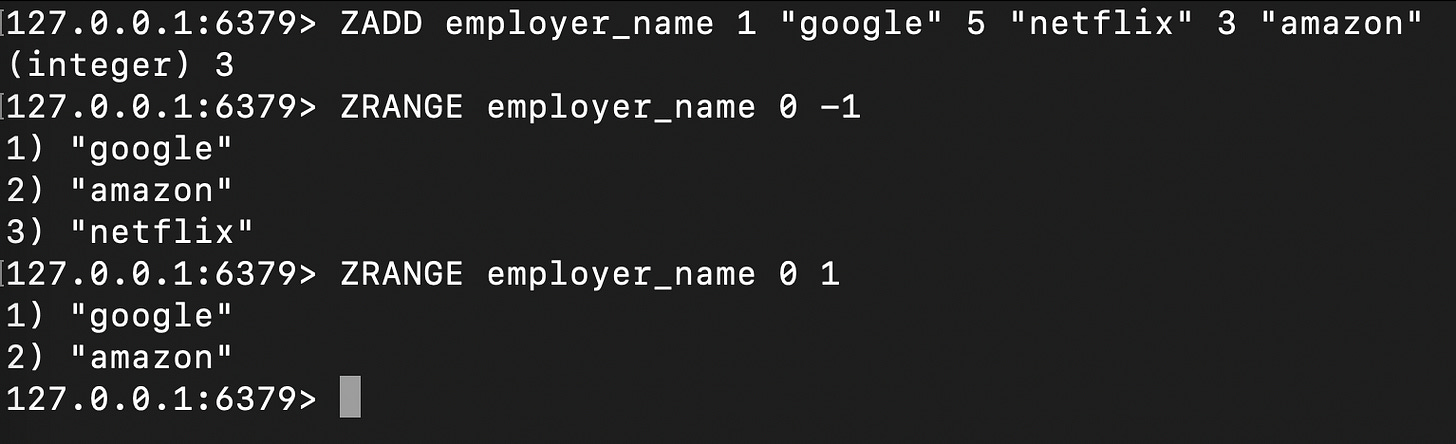
SortedSets
Sorted sets are similar to sets but with an associated score for each element. Elements are sorted in ascending order based on their scores.
These can be used for maintaining leaderboards, ranking systems, prioritizing tasks, and implementing range queries based on scores.
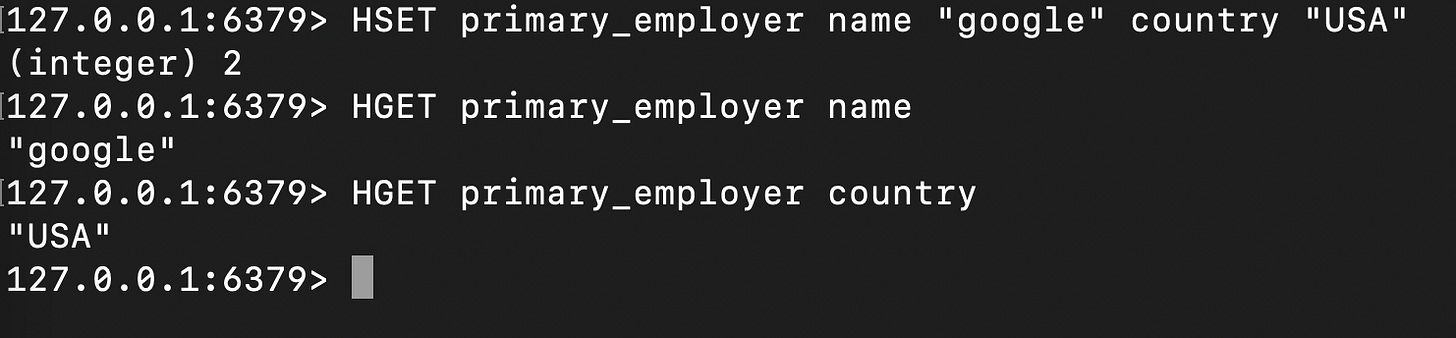
Hashes
Hashes are maps between fields and values, where each field-value pair is stored within a single key.
These can be used for representing objects, records, dictionaries, and nested data structures. Commonly used for storing user profiles, product details, configuration settings, caching data, and representing nested data structures.
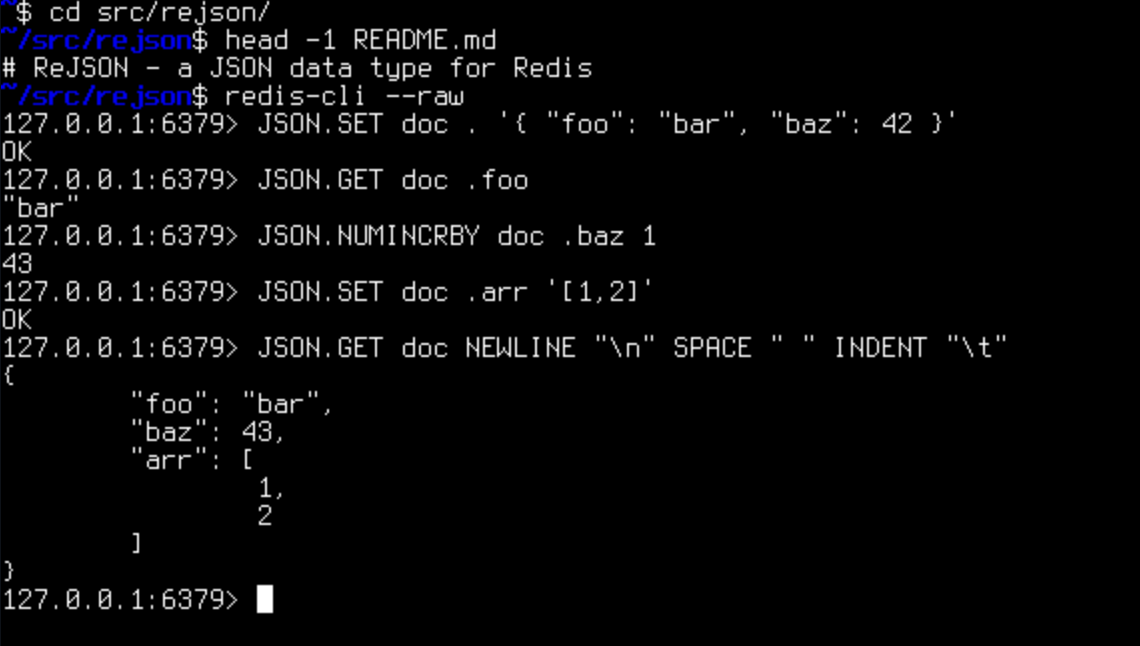
Rejson
ReJSON is a Redis module that adds support for storing, querying, and manipulating JSON data directly within Redis. It enables Redis to act as a JSON document store, providing efficient storage, retrieval, indexing, and querying of JSON documents.
These can be used for nested JSON structures, and JSON Path expressions for querying, and ensuring atomicity and consistency for JSON operations.